DC CIRCUIT FAULTS
Basic DC Theory
DC CIRCUIT FAULTS
Faults within a DC circuit will cause various effects, depending upon the nature
of the fault. An understanding of the effects of these faults is necessary to fully
understand DC circuit operation.
EO 1.16
DESCRIBE the voltage and current effects of an open
in a DC circuit.
EO 1.17
DESCRIBE the voltage and current effects in a shorted
DC circuit.
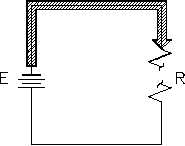
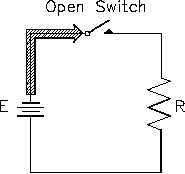
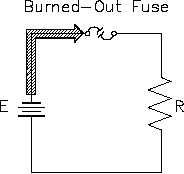
Open Circuit (Series)
A circuit must have a "complete" path for current flow, that is, from the negative side to the
positive side of a power source. A series circuit has only one path for current to flow. If this
path is broken, no current flows, and the circuit becomes an open circuit (Figure 53).
Circuits can be opened deliberately, such as by the use of a switch, or they may be opened by
Figure 53 Open Series Circuit
a defect, such as a broken wire or a burned-out resistor.
Since no current flows in an open series circuit, there are no voltage drops across the loads. No
power is consumed by the loads, and total power consumed by the circuit is zero.
ES-02
Page 66
Rev. 0