Pumps
DOE-HDBK-1018/1-93
POSITIVE DISPLACEMENT PUMPS
Principle of Operation
All positive displacement pumps operate on the same basic principle. This principle can be most
easily demonstrated by considering a reciprocating positive displacement pump consisting of a
single reciprocating piston in a cylinder with a single suction port and a single discharge port as
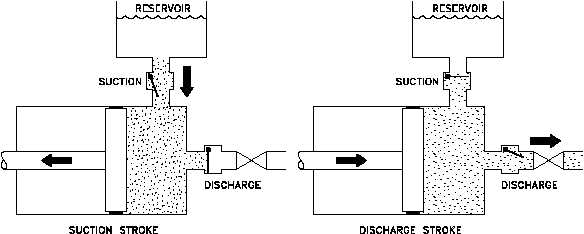
shown in Figure 12. Check valves in the suction and discharge ports allow flow in only one
direction.
During the suction stroke, the piston moves to the left, causing the check valve in the suction
Figure 12 Reciprocating Positive Displacement Pump Operation
line between the reservoir and the pump cylinder to open and admit water from the reservoir.
During the discharge stroke, the piston moves to the right, seating the check valve in the suction
line and opening the check valve in the discharge line. The volume of liquid moved by the
pump in one cycle (one suction stroke and one discharge stroke) is equal to the change in the
liquid volume of the cylinder as the piston moves from its farthest left position to its farthest
right position.
Reciprocating Pumps
Reciprocating positive displacement pumps are generally categorized in four ways: direct-acting
or indirect-acting; simplex or duplex; single-acting or double-acting; and power pumps.
Rev. 0
ME-03
Page 19