Basic DC Theory
DC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS
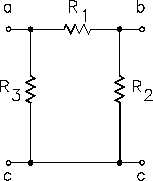
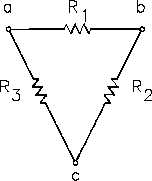
The network shown in Figure 48 is called p (pi) or D (delta) because the shapes resemble Greek
letters p and W. These are different names for the same network.
Figure 48
p (pi) or D (delta) Network
In order to analyze the circuits, it may be helpful to convert Y to D, or D to Y, to simplify the
solution. The formulas that will be used for these conversions are derived from Kirchhoff’s laws.
The resistances in these networks are shown in a three-terminal network. After we use the
conversion formulas, one network is equivalent to the other because they have equivalent
resistances across any one pair of terminals (Figure 49).
D to Y conversion:
Ra
R1R3
R1
R2
R3
Rb
R1R2
R1
R2
R3
Rc
R2R3
R1
R2
R3
Rule 1:
The resistance of any branch of a Y network is equal to the product of the two
adjacent sides of a D network, divided by the sum of the three D resistances.
Rev. 0
Page 61
ES-02