Basic DC Theory
KIRCHHOFF’S LAWS
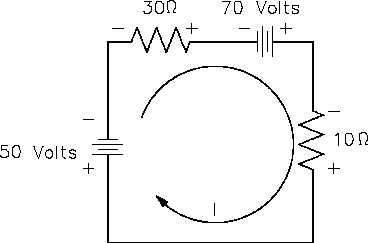
For example, what is the current flow in Figure 34? Assume that the current is flowing in the
direction shown.
Figure 34 Using Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law to find Current
with Multiple Battery Sources
Using Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law:
Esource
IR
50
70
30I
10I
20
40I
I
20
40
I
0.5
The result is negative. The current is actually 0.5 ampere in the opposite direction to that of the
assumed direction.
Kirchhoff’s Current Law
Kirchhoff’s second law is called his current law and states: "At any junction point in a circuit,
the current arriving is equal to the current leaving." Thus, if 15 amperes of current arrives at a
junction that has two paths leading away from it, 15 amperes will divide among the two
branches, but a total of 15 amperes must leave the junction. We are already familiar with
Kirchhoff’s current law from parallel circuits, that is, the sum of the branch currents is equal to
the total current entering the branches, as well as the total current leaving the branches
(Figure 35).
Rev. 0
Page 45
ES-02