?
GENERAL CORROSION
DOE-HDBK-1015/1-93
Corrosion
CH-02
Rev. 0
Page 14
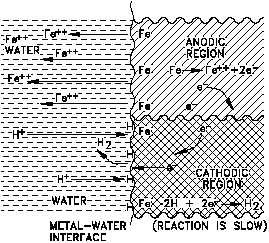
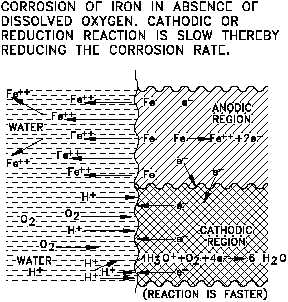
Figure 6 Representation of Cathodic Depolarization
by Oxygen
The overall reaction can be obtained by combining Equations (2-4) and (2-11).
The controlling step is believed to be
diffusion of O to the metal surface
2
where it can react directly with iron or
with FeO.
(2-12)
(2-13)
Oxygen, therefore, has two effects: it
removes the polarizing layer of atomic
hydrogen, and it can react directly with
the metal or metal oxide; thus, the
corrosion rate increases. Substances,
such as O in this case, that remove the
2
absorbed atomic hydrogen are called
depolarizers. The depolarizing effect of
O is illustrated in Figure 6.
2
The effect of the pH of water to which
iron or steel is exposed is influenced by
temperature in the following manner.
The potential of hydrogen or symbol
(pH) is defined as the negative logarithm
of
the
hydrogen
concentration,
represented as [H ] in moles/liter.
+
pH = -log [H ]+
The pH value is used to represent the
acidity of a solution.