CHEMISTRY PARAMETERS
DOE-HDBK-1015/2-93
Reactor Water Chemistry
CH-03
Rev. 0
Page 18
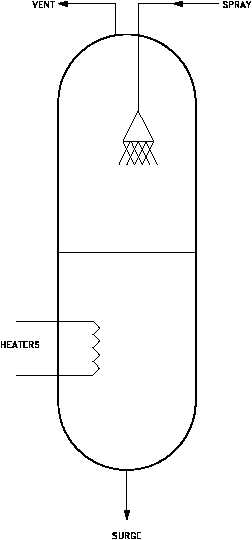
Figure 3 Pressurizer
Total Gas
Total gas concentration in the reactor coolant
system is another parameter of concern.
Total gas is the sum of all gases contained in
the coolant system and is made up primarily
of hydrogen (H ), nitrogen (N ), argon (Ar),
2
2
and oxygen (O ). The small amounts of
2
fission gases (Kr and Xe) normally present in
the system may also contribute to the total gas
concentration;
however,
under
normal
conditions these are essentially undetectable.
Total gas is of concern because high
concentrations can result in the formation of
gas pockets in areas that are high points of the
system where low or stagnant flow conditions
exist. Of particular concern in PWR facilities
are the erosion and corrosion that may occur
on the impellers of the primary coolant
pumps. As the concentration of gas is
increased, the probability of the gas coming
out of solution in significant amounts in areas
of low pressure is also increased. This low
pressure condition exists at the inlet to the
primary coolant pump impeller (where
centrifugal pumps are utilized). As these gas
bubbles are forced back into solution on the
high pressure side of the impeller, erosion can
occur as a result of the gas bubble impinging
on the impeller. In extreme concentrations of
total gas, loss of pump priming and cavitation
can occur with resultant mechanical pump
damage.
Reduction of total gas concentrations in PWRs is normally accomplished by the venting of a
steam space. In those facilities utilizing a pressurizer, the steam space in the top of the
pressurizer is designed to accomplish this venting operation either continuously or
intermittently. This process of reducing the total gas concentration is generally referred to as
degassification. A typical PWR pressurizer with degassification piping is shown in Figure 3.
Degassification is not normally required in a BWR because of its design. As discussed
previously, the boiling action in the reactor vessel strips dissolved gases from the water, and
they are continuously removed in the condensing phase of the energy cycle.