Heat Exchangers
DOE-HDBK-1018/1-93
TYPES OF HEAT EXCHANGERS
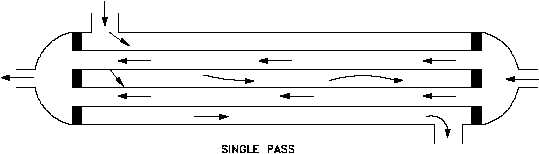
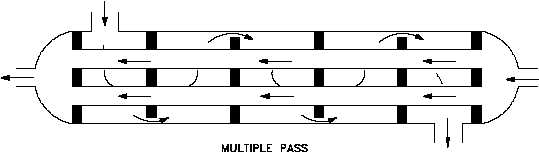
Figure 6 Single and Multi-Pass Heat Exchangers
Heat exchangers are also classified by their function in a particular system. One common
classification is regenerative or nonregenerative. A regenerative heat exchanger is one in which
the same fluid is both the cooling fluid and the cooled fluid, as illustrated in Figure 7. That is,
the hot fluid leaving a system gives up its heat to "regenerate" or heat up the fluid returning to
the system. Regenerative heat exchangers are usually found in high temperature systems where
a portion of the system's fluid is removed from the main process, and then returned. Because
the fluid removed from the main process contains energy (heat), the heat from the fluid leaving
the main system is used to reheat (regenerate) the returning fluid instead of being rejected to an
external cooling medium to improve efficiency. It is important to remember that the term
regenerative/nonregenerative only refers to "how" a heat exchanger functions in a system, and
does not indicate any single type (tube and shell, plate, parallel flow, counter flow, etc.).
Rev. 0
ME-02
Page 9