Reactor Theory (Reactor Operations)
DOE-HDBK-1019/2-93
REACTOR OPERATION
The previous examples discuss changes in radial power distribution. Large variations also exist
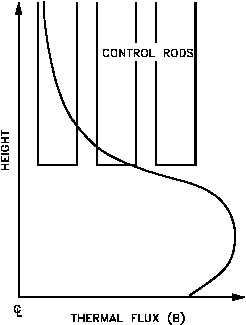
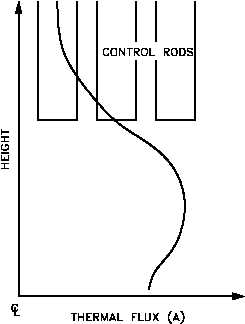
in axial power distribution. Figure 6(A) illustrates the power distribution that may exist for a
reactor with a cylindrical geometry. The control rods in this reactor are inserted from the top,
and the effect of inserting control rods further is shown in Figure 6(B). The thermal flux is
largely suppressed in the vicinity of the control rods, and the majority of the power is generated
low in the core. This flux profile can be flattened by the use of axial fuel and/or poison zoning.
Figure 6 Effect of Control Rod Position on Axial Flux Distribution
Power Tilt
A power tilt, or flux tilt, is a specific type of core power distribution problem. It is a
non-symmetrical variation of core power in one quadrant of the core relative to the others. The
power in one portion might be suppressed by over-insertion of control rods in that portion of the
core, which, for a constant overall power level, results in a relatively higher flux in the
remainder of the core. This situation can lead to xenon oscillations, which were previously
discussed.
Rev. 0
NP-04
Page 27