ATOM AND ITS FORCES
Basic Electrical Theory
The proton is the fundamental positive
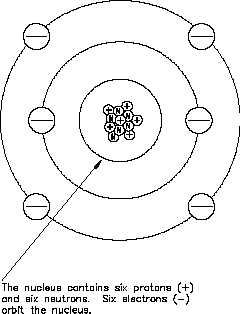
Figure 2 The Carbon Atom
charge (+) of electricity and is located in
the nucleus. The number of protons in
the nucleus of any atom specifies the
atomic number of that atom or of that
element. For example, the carbon atom
contains six protons in its nucleus;
therefore, the atomic number for carbon is
six, as shown in Figure 2.
In its natural state, an atom of any
element contains an equal number of
electrons and protons.
The negative
charge (-) of each electron is equal in
magnitude to the positive charge (+) of
each proton; therefore, the two opposite
charges cancel, and the atom is said to be
electrically neutral, or in balance.
Electrostatic Force
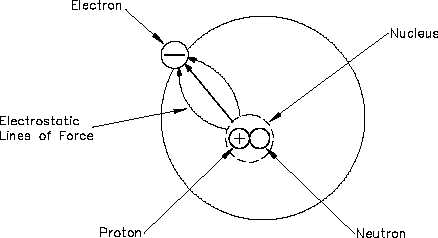
One of the mysteries of the atom is that the electron and the nucleus attract each other. This
attraction is called electrostatic force, the force that holds the electron in orbit. This force may
be illustrated with lines as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3 Electrostatic Force
ES-01
Page 2
Rev. 0