Basic AC Theory
AC GENERATION ANALYSIS
Example 2:
The peak current in an AC circuit is 10 amps. What is the average value of
current in the circuit?
Iav = 0.637 Imax
Iav = 0.637 (10 amps)
Iav = 6.37 amps
Phase Angle
Phase angle is the fraction of a cycle, in degrees, that has gone by since a voltage or current has
passed through a given value. The given value is normally zero. Referring back to Figure 3,
take point 1 as the starting point or zero phase. The phase at Point 2 is 30°, Point 3 is 60°, Point
4 is 90°, and so on, until Point 13 where the phase is 360°, or zero. A term more commonly
used is phase difference. The phase difference can be used to describe two different voltages that
have the same frequency, which pass through zero values in the same direction at different times.
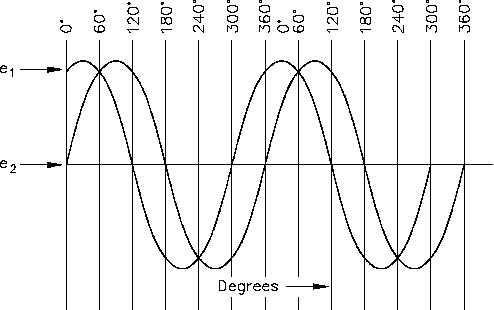
In Figure 5, the angles along the axis indicate the phases of voltages e1 and e2 at any point in
time. At 120°, e1 passes through the zero value, which is 60° ahead of e2 (e2 equals zero at
180°). The voltage e1 is said to lead e2 by 60 electrical degrees, or it can be said that e2 lags e1
by 60 electrical degrees.
Figure 5 Phase Relationship
Rev. 0
Page 7
ES-07