Test Instruments & Measuring Devices
AMMETERS
Equation (14-4) is the mathematical representation of the current with the meter installed in the
circuit.
(14-4)
Iw
V
Ro
Rm
The accuracy of the ammeter KA is the ratio of the current when the meter is in the circuit, Iw,
to the current with the meter out of the circuit, Io. Equation (14-5) is the mathematical
representation for solving for the accuracy of the ammeter (KA).
(14-5)
KA
Iw
Io
By substitution laws, Equation (14-6) is a mathematical representation of the accuracy using
circuit resistance.
(14-6)
KA
V
Ro
Rm
Ro
V
Ro
Ro
Rm
The percent loading error is that percent of error due to loading effects that result from the added
resistance of the meter. Equation (14-7) is a mathematical representation of the percent loading
error.
% loading error = (1 - KA)(100 %)
(14-7)
A second error which occurs in an
Figure 7 Ammeter Accuracy
ammeter is calibration error.
Calibration error is an error that
occurs due to inaccurately marked
meter faces.
Typical values of
calibration error in terms of full
scale current are about 3 percent.
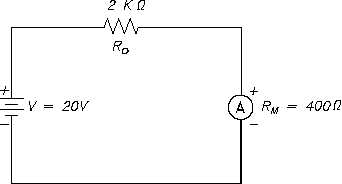
Example:
An ammeter, with a
10 mA full scale
deflection and an
internal resistance
of 400 W, is placed
in a circuit with a
20 V power source
and a 2 KW resistor (Figure 7).
Rev. 0
Page 11
ES-14