Radiation Detectors
RADIATION TYPES
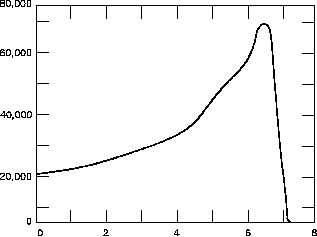
Figure 1 Alpha Particle Specific Ionization -vs- Distance Traveled in Air
Beta Particle
The beta particle is an ordinary electron or positron ejected from the nucleus of a beta-unstable
radioactive atom. The beta has a single negative or positive electrical charge and a very small
mass.
The interaction of a beta particle and an orbital electron leads to electrical excitation and
ionization of the orbital electron. These interactions cause the beta particle to lose energy in
overcoming the electrical forces of the orbital electron. The electrical forces act over long
distances; therefore, the two particles do not have to come into direct contact for ionization to
occur.
The amount of energy lost by the beta particle depends upon both its distance of approach to the
electron and its kinetic energy. Beta particles and orbital electrons have the same mass;
therefore, they are easily deflected by collision. Because of this fact, the beta particle follows
a tortuous path as it passes through absorbing material. The specific ionization of a beta particle
is low due to its small mass, small charge, and relatively high speed of travel.
Rev. 0
Page 5
IC-06