RADIATION TYPES
Radiation Detectors
Gamma Ray
The gamma ray is a photon of electromagnetic radiation with a very short wavelength and high
energy. It is emitted from an unstable atomic nucleus and has high penetrating power.
There are three methods of attenuating (reducing
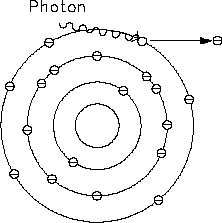
Figure 2 Photoelectric Effect
the energy level of) gamma-rays: photoelectric
effect, compton scattering, and pair production.
The photoelectric effect occurs when a low
energy gamma strikes an orbital electron, as
shown in Figure 2. The total energy of the
gamma is expended in ejecting the electron from
its orbit. The result is ionization of the atom and
expulsion of a high energy electron.
The photoelectric effect is most predominant with
low energy gammas and rarely occurs with
gammas having an energy above 1 MeV (million
electron volts).
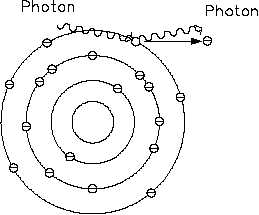
Compton scattering is an elastic collision between
Figure 3 Compton Scattering
an electron and a photon, as shown in Figure 3.
In this case, the photon has more energy than is
required to eject the electron from orbit, or it
cannot give up all of its energy in a collision with
a free electron. Since all of the energy from the
photon cannot be transferred, the photon must be
scattered; the scattered photon must have less
energy, or a longer wavelength. The result is
ionization of the atom, a high energy beta, and a
gamma at a lower energy level than the original.
Compton scattering is most predominant with
gammas at an energy level in the 1.0 to 2.0 MeV
range.
IC-06
Page 6
Rev. 0