Radiation Detectors
PROPORTIONAL COUNTER
PROPORTIONAL COUNTER
A proportional counter is a detector that operates in the proportional region.
EO 2.1
DESCRIBE the operation of a proportional counter to
include:
a.
Radiation detection
b.
Quenching
c.
Voltage variations
A proportional counter is a
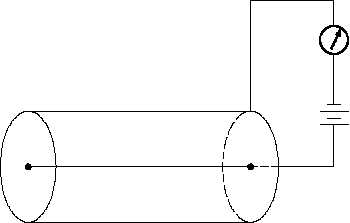
Figure 7 Proportional Counter
detector which operates in the
proportional region, as shown in
Figure 6. Figure 7 illustrates a
simplified proportional counter
circuit.
To be able to detect a single
particle, the number of ions
produced must be increased. As
voltage is increased into the
proportional region, the primary
ions acquire enough energy to
cause secondary ionizations (gas
amplification) and increase the
charge collected. These secondary
ionizations may cause further
ionization.
In this region, there is a linear relationship between the number of ion pairs collected and applied
voltage. A charge amplification of 104 can be obtained in the proportional region. By proper
functional arrangements, modifications, and biasing, the proportional counter can be used to
detect alpha, beta, gamma, or neutron radiation in mixed radiation fields.
To a limited degree, the fill-gas will determine what type of radiation the proportional counter
will be able to detect. Argon and helium are the most frequently used fill gases and allow for
the detection of alpha, beta, and gamma radiation. When detection of neutrons is necessary, the
detectors are usually filled with boron-triflouride gas.
The simplified circuit, illustrated in Figure 7, shows that the detector wall acts as one electrode,
while the other electrode is a fine wire in the center of the chamber with a positive voltage
applied.
Rev. 0
Page 19
IC-06