DOE-HDBK-1018/1-93
FUNDAMENTALS OF THE DIESEL CYCLE
Diesel Engine Fundamentals
The above numbers are ideal and provide a good example of what is occurring in an
engine during compression. In an actual engine, pressures reach only about 690 psia.
This is due primarily to the heat loss to the surrounding engine parts.
Fuel Injection
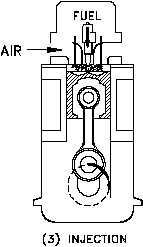
Figure 18 Fuel Injection
Fuel in a liquid state is injected into the cylinder at
a precise time and rate to ensure that the
combustion pressure is forced on the piston neither
too early nor too late, as shown in Figure 18. The
fuel enters the cylinder where the heated
compressed air is present; however, it will only
burn when it is in a vaporized state (attained
through the addition of heat to cause vaporization)
and intimately mixed with a supply of oxygen.
The first minute droplets of fuel enter the
combustion chamber and are quickly vaporized.
The vaporization of the fuel causes the air
surrounding the fuel to cool and it requires time
for the air to reheat sufficiently to ignite the
vaporized fuel. But once ignition has started, the
additional heat from combustion helps to further
vaporize the new fuel entering the chamber, as long as oxygen is present. Fuel
injection starts at 28 BTDC and ends at 3 ATDC; therefore, fuel is injected for
a duration of 31.
Power
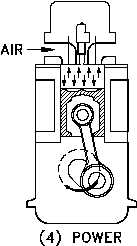
Both valves are closed, and the fresh air charge has
Figure 19 Power
been compressed. The fuel has been injected and
is starting to burn. After the piston passes TDC,
heat is rapidly released by the ignition of the fuel,
causing a rise in cylinder pressure. Combustion
temperatures are around 2336F.
This rise in
pressure forces the piston downward and increases
the force on the crankshaft for the power stroke as
illustrated in Figure 19.
The energy generated by the combustion process is
not all harnessed. In a two stroke diesel engine,
only about 38% of the generated power is
harnessed to do work, about 30% is wasted in the
form of heat rejected to the cooling system, and
about 32% in the form of heat is rejected out the
exhaust. In comparison, the four-stroke diesel
engine has a thermal distribution of 42% converted
ME-01
Rev. 0
Page 24