Basic Electrical Theory
ELECTRICAL TERMINOLOGY
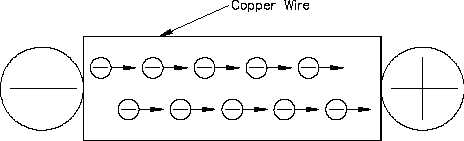
Figure 9 Electron Flow Through a Copper Wire with a Potential Difference
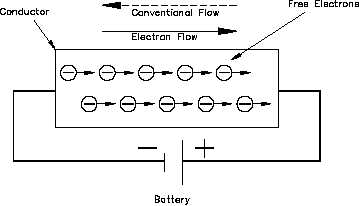
The direction of electron flow, shown in Figure 10, is from the negative (-) side of the battery,
through the wire, and back to the positive (+) side of the battery. The direction of electron flow
is from a point of negative potential to a point of positive potential. The solid arrow shown in
Figure 10 indicates the direction of electron flow. As electrons vacate their atoms during electron
current flow, positively charged atoms (holes) result. The flow of electrons in one direction
causes a flow of positive charges. The direction of the positive charges is in the opposite
direction of the electron flow. This flow of positive charges is known as conventional current
and is shown in Figure 10 as a dashed arrow. All of the electrical effects of electron flow from
negative to positive, or from a higher potential to a lower potential, are the same as those that
would be created by a flow of positive charges in the opposite direction. Therefore, it is
important to realize that both conventions are in use and that they are essentially equivalent; that
is, all effects predicted are the same. In this text, we will be using electron flow in our
discussions.
Figure 10 Potential Difference Across a Conductor Causes a Current to Flow
Rev. 0
Page 11
ES-01