METHODS OF PRODUCING VOLTAGE (ELECTRICITY)
Basic Electrical Theory
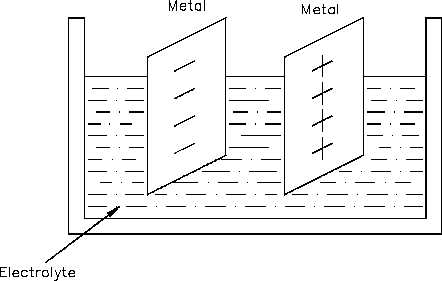
Figure 11 Voltaic Chemical Cell
Example:
A battery can maintain a potential difference between its positive and negative
terminals by chemical action. Various types of cells and batteries will be studied
in more detail in Module 4, Batteries.
Static Electricity
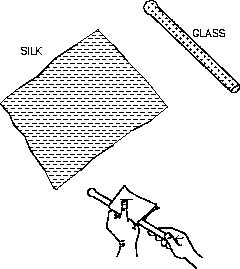
Figure 12 Static Electricity
Atoms with the proper number of electrons in
orbit around them are in a neutral state, or have
a "zero charge." A body of matter consisting of
these atoms will neither attract nor repel other
matter that is in its vicinity. If electrons are
removed from the atoms in this body of matter,
as happens due to friction when one rubs a glass
rod with a silk cloth, it will become electrically
positive as shown in Figure 12. If this body of
matter (e.g., glass rod) comes near, but not in
contact with, another body having a normal
charge, an electric force is exerted between them
because of their unequal charges. The existence
of this force is referred to as static electricity or
electrostatic force.
ES-01
Page 20
Rev. 0