CAPACITANCE
DC Circuits
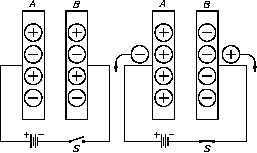
The two conductor plates of the capacitor, shown in Figure 11a, are electrically neutral, because
there are as many positive as negative charges on each plate. The capacitor, therefore, has no
charge.
Now, we connect a battery
Figure 11 Charging a Capacitor
across the plates (Figure
11b). When the switch is
closed (Figure 11c), the
negative charges on Plate
A are attracted to the
positive side of the battery,
while the positive charges
on Plate B are attracted to
the negative side of the
battery. This movement of
charges will continue until
the difference in charge
between Plate A and Plate
B is equal to the voltage of
the battery. This is now a
"charged capacitor." Capacitors store energy as an electric field between the two plates.
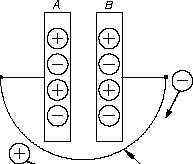
Because very few of the charges
Figure 12 Discharging a Capacitor
can cross between the plates, the
capacitor will remain in the
charged state even if the battery is
removed. Because the charges on
the opposing plates are attracted
by one another, they will tend to
oppose any changes in charge. In
this manner, a capacitor will
oppose any change in voltage felt
across it.
If we place a conductor across the
plates, electrons will find a path
back to Plate A, and the charges
will be neutralized again. This is
now a "discharged" capacitor (Figure 12).
ES-03
Page 10
Rev. 0