DC Circuits
INDUCTANCE
INDUCTANCE
Experiments investigating the unique behavioral characteristics of inductance led
to the invention of the transformer.
EO 1.1
DESCRIBE how current flow, magnetic field, and stored
energy in an inductor relate to one another.
EO 1.2
DESCRIBE how an inductor opposes a change in
current flow.
EO 1.3
Given a circuit containing inductors, CALCULATE total
inductance for series and parallel circuits.
EO 1.4
Given an inductive resistive circuit, CALCULATE the
time constant for the circuit.
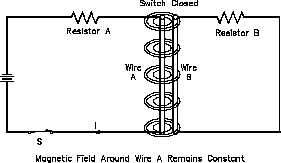
Inductors
An inductor is a circuit element
Figure 1 Induced EMF
that will store electrical energy in
the form of a magnetic field. It is
usually a coil of wire wrapped
around a core of permeable
material. The magnetic field is
generated when current is flowing
through the wire. If two circuits
are arranged as in Figure 1, a
magnetic field is generated around
Wire
A,
but
there
is
no
electromotive force (EMF) induced
into Wire B because there is no
relative
motion
between
the
magnetic field and Wire B.
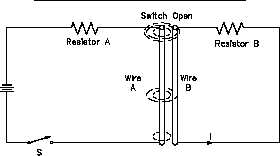
If we now open the switch, the
current stops flowing in Wire A,
and the magnetic field collapses.
As the field collapses, it moves
relative to Wire B. When this
occurs, an EMF is induced in Wire
B.
Rev. 0
Page 1
ES-03