METER MOVEMENTS
Test Instruments & Measuring Devices
A common variation of the D’Arsonval movement is the Weston movement, which uses
essentially the same principle built to a more rugged construction by employing jeweled supports
for the core and employing a heavier winding in the electromagnet. Remember that the
D’Arsonval movement is a DC device and can only measure DC current or AC current rectified
to DC.
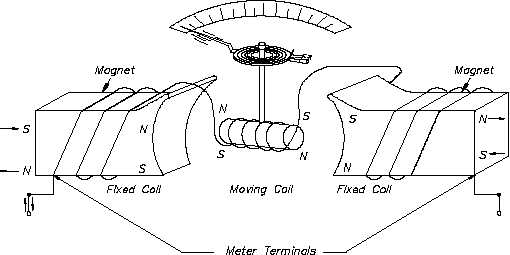
Electrodynamometer Movement
The electrodynamometer movement (Figure 2) has the same basic operating principle as the
D’Arsonval meter movement, except that the permanent magnet is replaced by fixed coils. The
moving coil and pointer, which are attached to the coil, are suspended between and connected
in series with the two field coils. The two field coils and moving coil are connected in series
such that the same current flows through each coil.
Figure 2 Electrodynamometer Movement
Current flow through the three coils in either direction causes a magnetic field to be produced
between the field coils. The same current flow through the moving coil causes it to act as a
magnet exerting a force against the spring. If the current is reversed, the field polarity and the
polarity of the moving coil reverse, and the force continues in the same direction. Due to this
characteristic of the electrodynamometer movement, it can be used in both AC and DC systems
to measure current. Some voltmeters and ammeters use the electrodynamometer. However, its
most important use is in the wattmeter, which will be discussed later in this module.
ES-14
Page 2
Rev. 0