Transformers
TRANSFORMER THEORY
Power loss in secondary = IS2RS = (20)2 (0.24) = 96 W
Example 2:
An open circuit test for core losses in a 10 kVA transformer [Example (1)] gives
a reading of 70 W. If the PF of the load is 90%, find efficiency at full load.
Solution:
Eff.
=
VS IS x PF
(VS IS x PF)
Copper Loss
Core Loss
x 100
VSIS
= transformer rating = 10 kVA = 10,000 VA
PF
= 0.90; Copper loss = 100 W; Core loss = 70 W
Eff
=
10,000 (0.90)
10,000 (0.90)
100
70
x 100
9000
9170
x 100
98.2%
Transformer Operation Under No-Load
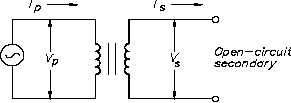
If the secondary of a transformer is left open-circuited (Figure 6), primary current is very low
and is called the no-load current. No-load current produces the magnetic flux and supplies the
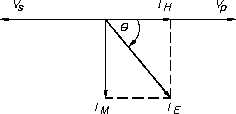
hysteresis and eddy current losses in the core. The no-load current (IE) consists of two
components: the magnetizing current (Im) and the core loss (IH). Magnetizing current lags
applied voltage by 90°, while core loss is in phase with the applied voltage (Figure 6b). VP and
VS are shown 180° out of phase. IH is very small in comparison with Im, and Im is nearly equal
to IE. No-load current, IE, is also referred to as exciting current.
Figure 6 Open-Circuit Secondary
Rev. 0
Page 13
ES-13