HEAD FLOW METERS
Flow Detectors
Pitot Tube
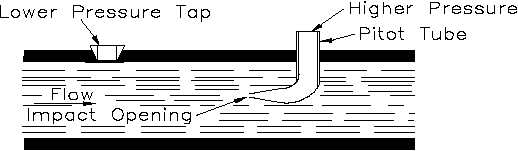
The pitot tube, illustrated in Figure 5, is another primary flow element used to produce a
differential pressure for flow detection. In its simplest form, it consists of a tube with an opening
at the end. The small hole in the end is positioned such that it faces the flowing fluid. The
velocity of the fluid at the opening of the tube decreases to zero. This provides for the high
pressure input to a differential pressure detector. A pressure tap provides the low pressure input.
Figure 5 Pitot Tube
The pitot tube actually measures fluid velocity instead of fluid flow rate. However, volumetric
flow rate can be obtained using Equation 4-4.
(4-4)
V
KAV
where
= volumetric flow rate (ft3/sec.)
A = area of flow cross-section (ft2)
V = velocity of flowing fluid (ft/sec.)
K = flow coefficient (normally about 0.8)
Pitot tubes must be calibrated for each specific application, as there is no standardization. This
type of instrument can be used even when the fluid is not enclosed in a pipe or duct.
IC-04
Page 6
Rev. 0