Process Controls
RESET (INTEGRAL) CONTROL SYSTEMS
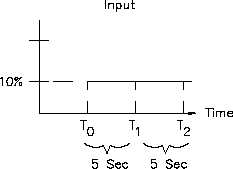
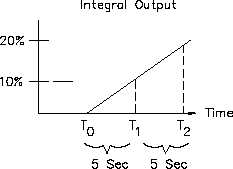
Figure 19 Integral Output for a Fixed Input
Example of an Integral Flow Control System
With integral control, the final control element’s position changes at a rate determined by the
amplitude of the input error signal. Recall that:
Error = Setpoint - Measured Variable
If a large difference exists between the setpoint and the measured variable, a large error results.
This causes the final control element to change position rapidly. If, however, only a small
difference exists, the small error signal causes the final control element to change position slowly.
Figure 20 illustrates a process using an integral controller to maintain a constant flow rate. Also
included is the equivalent block diagram of the controller.
Rev. 0
Page 29
IC-07