Process Controls
PROPORTIONAL CONTROL SYSTEMS
Steam is admitted to the heat exchanger to raise the temperature of the cold water supply. The
temperature detector monitors the hot water outlet and produces a 3 to 15 psi output signal that
represents a controlled variable range of 100o to 300oF. The controller compares the measured
variable signal with the setpoint and sends a 3 to 15 psi output to the final control element, which
is a 3-in control valve.
The controller has been set for a proportional band of 50%. Therefore, a 50% change in the
200oF span, or a change of 100oF, causes a 100% controller output change.
The proportional controller is reverse-acting so that the control valve throttles down to reduce
steam flow as the hot water outlet temperature increases; the control valve will open further to
increase steam flow as the water temperature decreases.
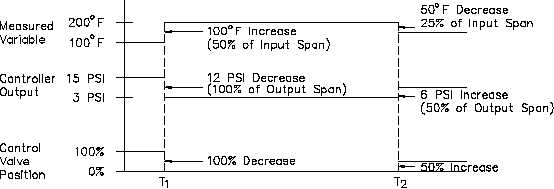
The combined action of the controller and control valve for different changes in the measured
variable is shown in Figure 17.
Initially, the measured variable value is equal to 100oF. The controller has been set so that this
Figure 17 Combined Controller and Final Control Element Action
value of measured variable corresponds to a 100% output, or 15 psi, which in turn, corresponds
to a "full open" control valve position.
At time t1, the measured variable increases by 100oF, or 50%, of the measured variable span.
This 50% controller input change causes a 100% controller output change due to the controller’s
proportional band of 50%. The direction of the controller output change is decreasing because
the controller is reverse-acting. The 100% decrease corresponds to a decrease in output for 15
psi to 3 psi, which causes the control valve to go from fully open to fully shut.
Rev. 0
Page 25
IC-07