TWO POSITION CONTROL SYSTEMS
Process Controls
Deviation is the difference between the setpoint of a process variable and its actual value. This
is a key term used when discussing various modes of control.
Four modes of control commonly used for most applications are:
proportional
proportional plus reset (PI)
proportional plus rate (PD)
proportional plus reset plus rate (PID)
Each mode of control has characteristic advantages and limitations. The modes of control are
discussed in this and the next several sections of this module.
In the proportional (throttling) mode, there is a continuous linear relation between value of the
controlled variable and position of the final control element. In other words, amount of valve
movement is proportional to amount of deviation.
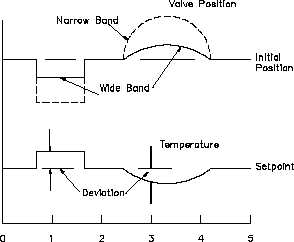
Figure 14 shows the relationship between valve position and controlled variable (temperature)
characteristics of proportional mode. Notice that valve position changes in exact proportion to
deviation. Also, the proportional mode responds only to amount of deviation and is insensitive
to rate or duration of deviation. At the 2 minute and 4 minute marks, when the temperature
returns to its setpoint value, the valve returns to its initial position. There is no valve correction
without deviation.
Figure 14 Relation Between Valve Position and Controlled
Variable Under Proportional Mode
IC-07
Page 20
Rev. 0