Process Controls
TWO POSITION CONTROL SYSTEMS
Example of Two Position Control
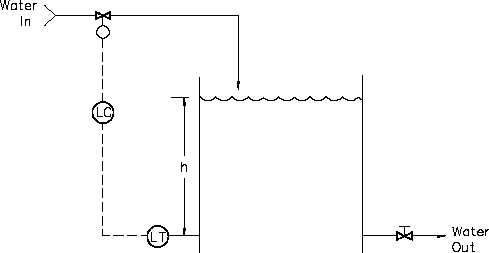
A system using a two position controller is shown in Figure 13.
Figure 13 Two Position Control System
The controlled process is the volume of water in the tank. The controlled variable is the level
in the tank. It is measured by a level detector that sends information to the controller. The
output of the controller is sent to the final control element, which is a solenoid valve, that
controls the flow of water into the tank.
As the water level decreases initially, a point is reached where the measured variable drops below
the setpoint. This creates a positive error signal. The controller opens the final control element
fully. Water is subsequently injected into the tank, and the water level rises. As soon as the
water level rises above the setpoint, a negative error signal is developed. The negative error
signal causes the controller to shut the final control element. This opening and closing of the final
control element results in a cycling characteristic of the measured variable.
Modes of Automatic Control
The mode of control is the manner in which a control system makes corrections relative to an
error that exists between the desired value (setpoint) of a controlled variable and its actual value.
The mode of control used for a specific application depends on the characteristics of the process
being controlled. For example, some processes can be operated over a wide band, while others
must be maintained very close to the setpoint. Also, some processes change relatively slowly,
while others change almost immediately.
Rev. 0
Page 19
IC-07