PROPORTIONAL CONTROL SYSTEMS
Process Controls
PROPORTIONAL CONTROL SYSTEMS
Proportional control is also referred to as throttling control.
EO 1.4
DESCRIBE the characteristics of the following types of
automatic control systems:
b.
Proportional control system
Control Mode
In the proportional control mode, the final control element is throttled to various positions that
are dependent on the process system conditions. For example, a proportional controller provides
a linear stepless output that can position a valve at intermediate positions, as well as "full open"
or "full shut." The controller operates within a band that is between the 0% output point and the
100% output point and where the output of the controller is proportional to the input signal.
Proportional Band
With proportional control, the final control element has a definite position for each value of the
measured variable.
In other words, the output has a linear relationship with the input.
Proportional band is the change in input required to produce a full range of change in the output
due to the proportional control action. Or simply, it is the percent change of the input signal
required to change the output signal from 0% to 100%.
The proportional band determines the
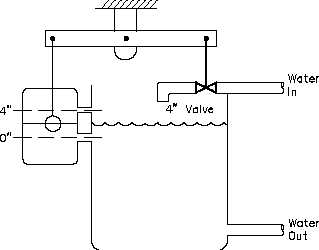
Figure 15 Proportional System Controller
range of output values from the
controller that operate the final control
element. The final control element acts
on
the
manipulated
variable
to
determine the value of the controlled
variable.
The controlled variable is
maintained within a specified band of
control points around a setpoint.
To demonstrate, let’s look at Figure 15.
In this example of a proportional level
control system, the flow of supply water
into the tank is controlled to maintain
the tank water level within prescribed
limits. The demand that disturbances
placed on the process system are such
IC-07
Page 22
Rev. 0