EFFECTS OF RADIATION
DOE-HDBK-1015/2-93
Reactor Water Chemistry
ON WATER CHEMISTRY (SYNTHESIS)
CH-03
Rev. 0
Page 8
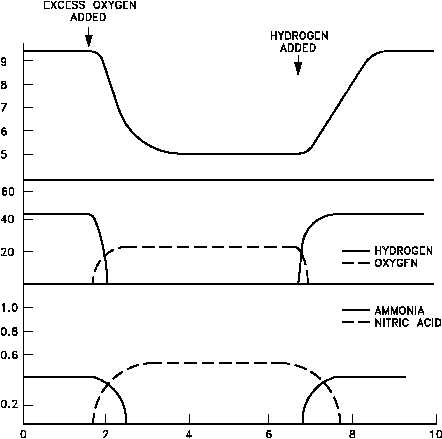
Figure 1 Change in pH, Gas Concentration, and Nitrogen Compounds
With Excess Oxygen Added
Normally, the amount of hydrogen maintained in the reactor coolant, in conjunction with other
precautions employed, greatly reduces the probability that the amount of oxygen entering the
coolant will be sufficient to lead to Reaction (3-16). If a large amount of air were accidentally
added to the reactor coolant, one solution would be to add more hydrogen. The added hydrogen
would react with remaining oxygen, disrupting the equilibrium of Reaction (3-16) causing the
reverse step of that reaction to occur. When all the oxygen has been removed, H and N could
2
2
react by Reaction (3-14) and help reestablish a basic pH. The relationship between these
reactions and pH following the initial oxygen addition, and a subsequent hydrogen addition, is
illustrated in Figure 1.