APPENDIX A
DOE-HDBK-1017/1-93
Properties of Metals
Organics are easily permeated by tritium (gas or water) and are therefore subject to disruption
of their bulk chemistries. There are few or no mechanisms for rapidly delocalizing beta energy,
and substantial mobility of organic chains occur within polymer structures (particularly
amorphous regions). Once formed, reactive organic intermediates can thus react with each other.
These effects are important when considering the design of tritium systems. Damage to
components, such as gaskets, valve tips, and O-rings, must be carefully considered. Component
failure during service can cause a major release of tritium. Because elastomer seals often
become embrittled, maintenance on nearby sections of piping may cause seals to develop leaks
as the result of mechanical movement in the seal area.
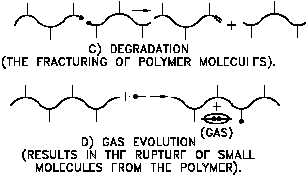
Figure A-1 illustrates several polymer
Figure A-1 Modifications to Polymer Chains
Due to Irradiation
chain modifications that take place
following activation by beta radiation to
ionic or excited species. Cross-linking
and degradation are the most important
processes to the mechanical properties of
the polymer. These both compete in a
material, but those polymers that are
most sterically hindered appear to
preferentially degrade. Steric hindrance
prevents neighboring chains from linking
and also imparts structural strains that are
relieved upon chain scissioning. Cross-
linking is noted mechanically by an
increase in tensile strength and a decrease
in elongation, whereas degradation is
evidenced by a decrease in tensile
strength, an increase in elongation, and
softening of the polymer to a gummy
consistency.
Several factors effect polymer stability.
First,
energy-delocalizing
aromatic
structural groups increase polymer
stability by distributing energies of
excited states. In addition, halogen atoms
within polymers generate free radicals
and thus promote radiation damage.
MS-02
Page A-6
Rev. 0-A