Miscellaneous Mechanical Components
DOE-HDBK-1018/2-93
DEMINERALIZERS
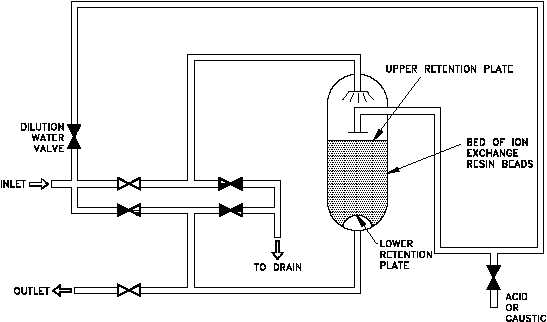
Figure 13 illustrates a single-bed demineralizer. When in use, water flows in through the inlet
to a distributor at the top of the tank. The water flows down through the resin bed and exits out
through the outlet. A support screen at the bottom prevents the resin from being forced out of
the demineralizer tank.
Single-Bed Regeneration
Figure 13 Single-Bed Demineralizer
The regeneration of a single-bed ion exchanger is a three-step process. The first step is a
backwash, in which water is pumped into the bottom of the ion exchanger and up through the
resin. This fluffs the resin and washes out any entrained particles. The backwash water goes
out through the normal inlet distributor piping at the top of the tank, but the valves are set to
direct the stream to a drain so that the backwashed particles can be pumped to a container for
waste disposal.
The second step is the actual regeneration step, which uses an acid solution for cation units and
caustic solution for anion units. The concentrated acid or caustic is diluted to approximately
10% with water by opening the dilution water valve, and is then introduced through a
distribution system immediately above the resin bed. The regenerating solution flows through
the resin and out the bottom of the tank to the waste drain.
The final step is a rinsing process, which removes any excess regenerating solution. Water is
pumped into the top of the tank, flows down through the resin bed and out at the bottom drain.
Rev. 0
ME-05
Page 25