DOE-HDBK-1019/2-93
SAMARIUM AND OTHER FISSION PRODUCT POISONS
Reactor Theory (Nuclear Parameters)
The xenon-135 and samarium-149 mechanisms are dependent on their very large thermal neutron
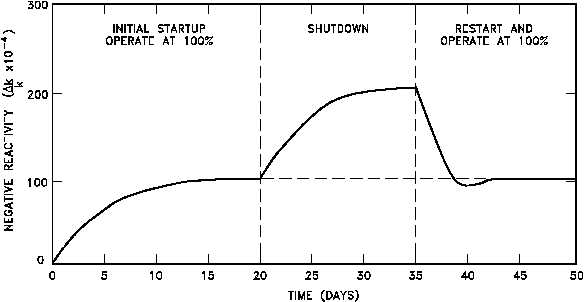
Figure 7 Behavior of Samarium-149 in a Typical Light Water Reactor
cross sections and only affect thermal reactor systems. In fast reactors, neither these nor any
other fission products have a major poisoning influence.
Other Neutron Poisons
There are numerous other fission products that, as a result of their concentration and thermal
neutron absorption cross section, have a poisoning effect on reactor operation. Individually, they
are of little consequence, but "lumped" together they have a significant impact. These are often
characterized as "lumped fission product poisons" and accumulate at an average rate of 50 barns
per fission event in the reactor.
In addition to fission product poisons, other materials in the reactor decay to materials that act
as neutron poisons. An example of this is the decay of tritium to helium-3. Since tritium has
a half-life of 12.3 years, normally this decay does not significantly affect reactor operations
because the rate of decay of tritium is so slow. However, if tritium is produced in a reactor and
then allowed to remain in the reactor during a prolonged shutdown of several months, a
NP-03
Rev. 0
Page 46