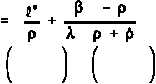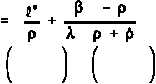¯
¯
eff
¯
eff
eff
prompt
term
delayed
term
¯
eff
Reactor Theory (Reactor Operations)
DOE-HDBK-1019/2-93
REACTOR KINETICS
Rev. 0
NP-04
Page 21
Summary
The important information in this chapter is summarized below.
Reactor Kinetics Summary
Reactor period is the time required for reactor power to change by a factor of e
(2.718).
Doubling time is the time required for reactor power to double.
Reactor startup rate is the number of factors of ten that reactor power changes in
one minute.
The delayed neutron fraction ( ) is the fraction of all fission neutrons that are
born as delayed neutrons for a particular type of fuel (that is, uranium-235 and
plutonium-239).
The average delayed neutron fraction ( ) is the weighted average of the total
delayed neutron fractions of the different types of fuel used in a particular reactor.
The effective delayed neutron fraction (
) is the average delayed neutron
fraction multiplied by an Importance Factor which accounts for the fact that
delayed neutrons are born at lower average energies than fast neutrons.
The reactor period equation is stated below.
where:
= reactor period
*
= prompt generation lifetime
= effective delayed neutron fraction
= reactivity
= effective delayed neutron precursor decay constant
eff
= rate of change of reactivity