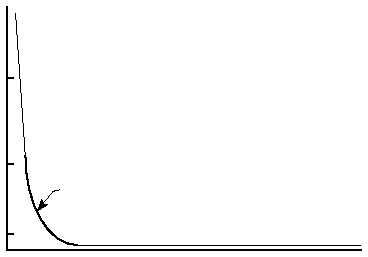
C
C/2
C/10
0
0
Time in hours
Constant voltage
charge rate
Lead-Acid Storage Batteries
DOE-HDBK-1084-95
MAINTENANCE
Rev. 0
Page 31
Batteries
Figure 16. Charge rate versus time for a typical constant-voltage charger.
charger to minimize the effects of overcharge on batteries having infrequent
discharges as described below.
Float Charging
Float charging is most commonly used for backup and emergency power
applications where the discharge of the battery is infrequent. During float charging
the charger, battery, and load are connected in parallel. The charger operates off
the normal power supply which provides current to the load during operation. In
the event of normal power supply failure, the battery provides backup power until
the normal power supply is restored. Since most equipment requires alternating
current, a rectifier circuit is usually added between the battery and the load. Float
chargers are typically constant-voltage chargers that operate at a low voltage.
Operating the charger at a low voltage, usually less than about 2.4 V per cell, keeps
the charging current low and thus minimizes the damaging effects of high-current
overcharging.
For valve-regulated batteries, an important consideration when float charging is
the possible occurrence of a phenomena called "thermal runaway" (discussed in the
definitions and the section on Sealed Lead-Acid Batteries). The best way of
preventing thermal runaway is through the use of a temperature-compensated
battery charger. A temperature-compensated charger adjusts the float voltage
based upon battery temperature. Temperature-compensated chargers will increase
the reliability and prolong the life of the battery/charger system. They are
especially useful for batteries located in areas where temperatures may be
significantly above ambient conditions.