BASIC DC CIRCUIT CALCULATIONS
Basic DC Theory
Resistance in Parallel
Total resistance in a parallel circuit can be found by applying Ohm’s Law. Divide the voltage
across the parallel resistance by the total line current as shown in equation (2-9).
(2-9)
RT
V
IT
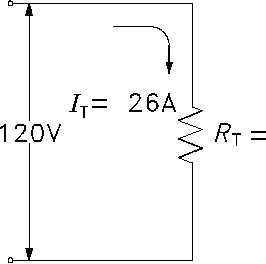
Example:
Find the total resistance of the circuit shown in Figure 25 if the line voltage is
120 V and total current is 26A.
RT
V
IT
120
26
4.62 W
The total load connected to a 120 V source is the same as the single "equivalent resistance" of
4.62W connected across the source (Figure 26). Equivalent resistance is the total resistance a
combination of loads present to a circuit.
Figure 26 Equivalent Resistance in a Parallel Circuit
ES-02
Page 32
Rev. 0