Basic DC Theory
DC SOURCES
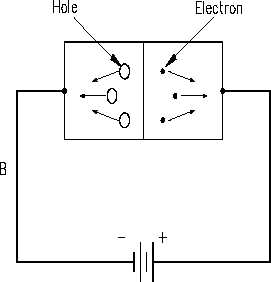
When a hole combines with an electron, or an electron combines with a hole near the p-n
junction, an electron from an electron-pair bond in the p-type material breaks its bond and enters
the positive side of the source. Simultaneously, an electron from the negative side of the source
enters the n-type material (Figure 4C). This produces a flow of electrons in the circuit.
Reverse Bias
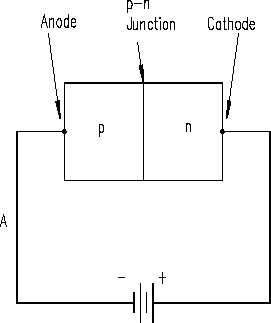
Reverse biasing occurs when the diode’s anode is connected to the negative side of the source,
and the cathode is connected to the positive side of the source (Figure 5A). Holes within the
p-type material are attracted toward the negative terminal, and the electrons in the n-type material
are attracted to the positive terminal (Figure 5B). This prevents the combination of electrons and
holes near the p-n junction, and therefore causes a high resistance to current flow. This
resistance prevents current flow through the circuit.
Figure 5 Reverse-Biased Diode
Rev. 0
Page 7
ES-02