POWER TRIANGLE
Basic AC Power
Total Power
The total power delivered by the source is the apparent power. Part of this apparent power,
called true power, is dissipated by the circuit resistance in the form of heat. The rest of the
apparent power is returned to the source by the circuit inductance and capacitance.
Power Factor
Power factor (pf) is the ratio between true power and apparent power. True power is the power
consumed by an AC circuit, and reactive power is the power that is stored in an AC circuit.
Cosq is called the power factor (pf) of an AC circuit. It is the ratio of true power to apparent
power, where q is the phase angle between the applied voltage and current sine waves and also
between P and S on a power triangle (Figure1). Equation (9-4) is a mathematical representation
of power factor.
(9-4)
cosq
P
S
where
cosq
=
power factor (pf)
P
=
true power (watts)
S
=
apparent power (VA)
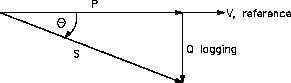
Power factor also determines what part of the
Figure 2 Lagging Power Factor
apparent power is real power. It can vary
from 1, when the phase angle is 0°, to 0,
when the phase angle is 90°. In an inductive
circuit, the current lags the voltage and is said
to have a lagging power factor, as shown in
Figure 2.
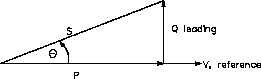
In a capacitive circuit, the current leads the voltage
Figure 3 Leading Power Factor
and is said to have a leading power factor, as
shown in Figure 3.
A mnemonic memory device, "ELI the ICE man,"
can be used to remember the voltage/current
relationship in AC circuits.
ELI refers to an
inductive circuit (L) where current (I) lags voltage
(E). ICE refers to a capacitive circuit (C) where
current (I) leads voltage (E).
ES-09
Page 4
Rev. 0