Electrical Distribution Systems
CIRCUIT BREAKERS
CIRCUIT BREAKERS
A circuit breaker is a device that is used to completely disconnect a circuit when
any abnormal condition exists. The circuit breaker can be designed to actuate
under any undesirable condition.
EO 1.3
STATE the purpose of circuit breakers.
EO 1.4
Given a simple schematic of a circuit breaker control
circuit, DESCRIBE the operation of that breaker
during remote operation and automatic tripping.
EO 1.5
LIST the three most widely-used protective features
that may be incorporated into a circuit breaker
control circuit.
Introduction
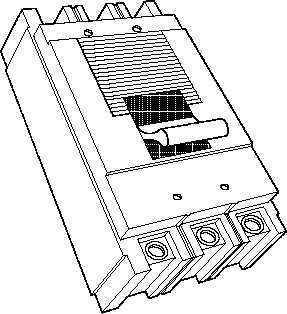
Figure 4 Molded Case Circuit Breaker
The purpose of a circuit breaker is to break the circuit and stop the current flow when the current
exceeds a predetermined value without causing damage to the circuit or the circuit breaker.
Circuit breakers are commonly used in place of fuses and sometimes eliminate the need for a
switch.
A circuit breaker differs
from a fuse in that it "trips" to break
the circuit and may be reset, while a
fuse melts and must be replaced.
Air circuit breakers (ACBs) are
breakers where the interruption of
the breaker contacts takes place in an
air environment. Oil circuit breakers
(OCBs) use oil to quench the arc
when the breaker contacts open.
Low-Voltage Air
Circuit Breakers
A low-voltage circuit breaker is one
which is suited for circuits rated at
600 volts or lower. One of the most
commonly used low-voltage air
circuit breakers is the molded case
circuit breaker (Figure 4).
Rev. 0
Page 7
ES-15