Electrical Distribution Systems
SYSTEM COMPONENTS AND PROTECTION DEVICES
Fuses
A fuse is a device that protects a circuit from an overcurrent condition only. It has a fusible link
directly heated and destroyed by the current passing through it. A fuse contains a current-
carrying element sized so that the heat generated by the flow of normal current through it does
not cause it to melt the element; however, when an overcurrent or short-circuit current flows
through the fuse, the fusible link will melt and open the circuit. There are several types of fuses
in use (Figure 3).
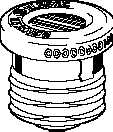
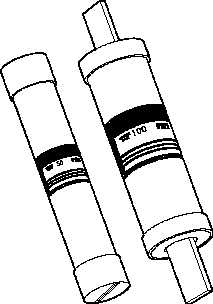
Figure 3 Types of Fuses
The plug fuse is a fuse that consists of a zinc or alloy strip, a fusible element enclosed in
porcelain or pyrex housing, and a screw base. This type of fuse is normally used on circuits
rated at 125 V or less to ground and has a maximum continuous current-carrying capacity of 30
amps.
The cartridge fuse is constructed with a zinc or alloy fusible element enclosed in a cylindrical
fiber tube with the element ends attached to a metallic contact piece at the ends of the tube. This
type of fuse is normally used on circuits rated at either 250 volts or 600 volts and has a
maximum continuous current-carrying capacity of 600 amps.
Rev. 0
Page 5
ES-15