Thermodynamics
CHANGE OF PHASE
Moisture Content
The moisture content of a substance is the opposite of its quality. Moisture (M) is defined as
the ratio of the mass of the liquid to the total mass of both liquid and vapor. The moisture of
the mixture in the previous paragraph would be 0.8 or 80%. The following equations show how
to calculate the moisture of a mixture and the relationship between quality and moisture.
(1-21)
M
mliquid
(mliquid
mvapor)
M = 1 - x
Saturated and Superheated Vapors
If a substance exists entirely as vapor at saturation temperature, it is called saturated vapor.
Sometimes the term dry saturated vapor is used to emphasize that the quality is 100%. When
the vapor is at a temperature greater than the saturation temperature, it is said to exist as
superheated vapor. The pressure and temperature of superheated vapor are independent
properties, since the temperature may increase while the pressure remains constant. Actually, the
substances we call gases are highly superheated vapors.
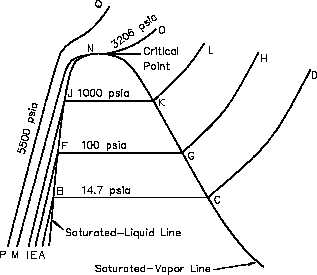
Constant Pressure Heat Addition
Consider the plot on the
Figure 7 T-V Diagram
temperature-volume diagram of
Figure
7,
viewing
the
constant-pressure
line
that
represents the states through
which
the
water
of
the
previous discussion passes as it
is heated from the initial state
of 14.7 psia and 60°F. Let
state A represent the initial
state and state B represent the
start of the saturated liquid line
(212°F). Therefore, line AB
represents the process in which
the liquid is heated from the
initial
temperature
to
the
saturation temperature.
Rev. 0
Page 35
HT-01