Thermodynamics
CHANGE OF PHASE
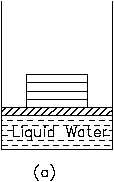
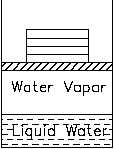
Figure 4 Piston-cylinder Arrangement
Saturation
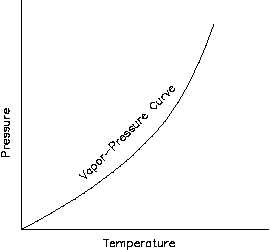
Figure 5 Vapor Pressure Curve
The term saturation defines a condition in which
a mixture of vapor and liquid can exist together
at a given temperature and pressure.
The
temperature at which vaporization (boiling) starts
to occur for a given pressure is called the
saturation temperature or boiling point. The
pressure at which vaporization (boiling) starts to
occur for a given temperature is called the
saturation pressure. For water at 212°F, the
saturation pressure is 14.7 psia and, for water at
14.7 psia, the saturation temperature is 212°F.
For a pure substance there is a definite
relationship between saturation pressure and
saturation temperature. The higher the pressure,
the higher the saturation temperature.
The
graphical representation of this relationship
between temperature and pressure at saturated
conditions is called the vapor pressure curve. A
typical vapor pressure curve is shown in Figure 5. The vapor/liquid mixture is at saturation when
the conditions of pressure and temperature fall on the curve.
Saturated and Subcooled Liquids
If a substance exists as a liquid at the saturation temperature and pressure, it is called a saturated
liquid.
Rev. 0
Page 33
HT-01