FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
Thermodynamics
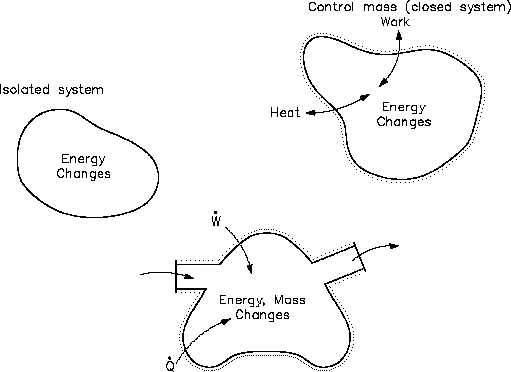
Heat and/or work can be directed into or out of the control volume. But, for convenience and
as a standard convention, the net energy exchange is presented here with the net heat exchange
assumed to be into the system and the net work assumed to be out of the system. If no mass
crosses the boundary, but work and/or heat do, then the system is referred to as a "closed"
system. If mass, work and heat do not cross the boundary (that is, the only energy exchanges
taking place are within the system), then the system is referred to as an isolated system. Isolated
and closed systems are nothing more than specialized cases of the open system. In this text, the
open system approach to the First Law of Thermodynamics will be emphasized because it is
more general. Also, almost all practical applications of the first law require an open system
analysis.
An understanding of the control volume concept is essential in analyzing a thermodynamic
problem or constructing an energy balance.
Two basic approaches exist in studying
Thermodynamics: the control mass approach and the control volume approach. The former is
referred to as the LeGrange approach and the latter as the Eulerian approach. In the control mass
concept, a "clump" of fluid is studied with its associated energies. The analyzer "rides" with the
clump wherever it goes, keeping a balance of all energies affecting the clump.
Figure 15 Control Volume Concepts
HT-01
Page 56
Rev. 0