PROPORTIONAL COUNTER
Radiation Detectors
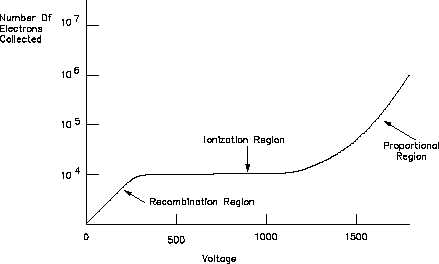
Figure 8 illustrates how the number of electrons collected varies with the applied voltage.
Figure 8 Gas Ionization Curve
When a single gamma ray interacts with the gas in the chamber, it produces a rapidly moving
electron which produces secondary electrons. About 10,000 electrons may be formed depending
on the gas used in the chamber. The applied voltage can be increased until the amount of
recombination is very low. However, further increases do not appreciably increase the number
of electrons collected. This region in which all 10,000 electrons are collected is the ionization
region.
As applied voltage is increased above 1000 V, the number of electrons becomes greater than the
initial 10,000. The additional electrons which are collected are due to gas amplification. As
voltage is increased, the velocity of the 10,000 electrons produced increases. However, beyond
a certain voltage, the 10,000 electrons are accelerated to such speeds that they have enough
energy to cause more ionization. This phenomenon is called gas amplification.
IC-06
Page 20
Rev. 0