Radiation Detectors
GAS-FILLED DETECTOR
GAS-FILLED DETECTOR
A gas-filled detector is used to detect incident radiation.
EO 1.4
DESCRIBE the principles of operation of a gas-filled
detector to include:
a.
How the electric field affects ion pairs
b.
How gas amplification occurs
The pulsed operation of the gas-filled detector illustrates the principles of basic radiation
detection. Gases are used in radiation detectors since their ionized particles can travel more
freely than those of a liquid or a solid. Typical gases used in detectors are argon and helium,
although boron-triflouride is utilized when the detector is to be used to measure neutrons. Figure
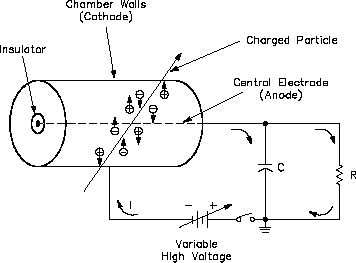
5 shows a schematic diagram of a gas-filled chamber with a central electrode.
Figure 5 Schematic Diagram of a Gas-Filled Detector
The central electrode, or anode, collects negative charges. The anode is insulated from the
chamber walls and the cathode, which collects positive charges. A voltage is applied to the
anode and the chamber walls. The resistor in the circuit is shunted by a capacitor in parallel, so
that the anode is at a positive voltage with respect to the detector wall. As a charged particle
passes through the gas-filled chamber, it ionizes some of the gas (air) along its path of travel.
The positive anode attracts the electrons, or negative particles. The detector wall, or cathode,
attracts the positive charges. The collection of these charges reduces the voltage across the
capacitor, causing a pulse across the resistor that is recorded by an electronic circuit. The voltage
applied to the anode and cathode determines the electric field and its strength.
Rev. 0
Page 11
IC-06