Radiation Detectors
SCINTILLATION COUNTER
SCINTILLATION COUNTER
The scintillation counter is a solid state radiation detector.
EO 2.7
DESCRIBE the operation of a scintillation counter to
include:
a.
Radiation detection
b.
Three classes of phosphors
c.
Photomultiplier tube operation
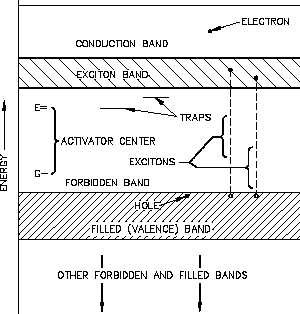
The scintillation counter is a solid state radiation detector which uses a scintillation crystal
(phosphor) to detect radiation and produce light pulses. Figure 24 is important in the explanation
of scintillation counter operation.
As
radiation
interacts
in
the
Figure 24 Electronic Energy Band of an Ionic Crystal
scintillation
crystal,
energy
is
transferred to bound electrons of the
crystal’s atoms. If the energy that is
transferred
is
greater
than
the
ionization energy, the electron enters
the conduction band and is free from
the binding forces of the parent atom.
This leaves a vacancy in the valence
band and is termed a hole. If the
energy transferred is less than the
binding energy, the electron remains
attached, but exists in an excited
energy state. Once again, a hole is
created in the valence band.
By
adding impurities during the growth of
the
scintillation
crystal,
the
manufacturer is able to produce
activator centers with energy levels
located within the forbidden energy
gap. The activator center can trap a
mobile electron, which raises the activator center from its ground state, G, to an excited state,
E. When the center de-excites, a photon is emitted. The activator centers in a scintillation
crystal are referred to as luminescence centers. The emitted photons are in the visible region of
the electromagnetic spectrum.
Rev. 0
Page 45
IC-06