DOE-HDBK-1016/2-93
ELECTRONIC DIAGRAMS, PRINTS, AND SCHEMATICS
Electronic Diagrams and Schematics
PR-04
Page 12
Rev. 0
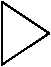
Figure 12 Example Blocks
Block Drawing Symbology
Not all electronics prints are drawn to the level of detail depicting the individual resistors and
capacitors, nor is this level of information always necessary. These simpler drawings are called
block diagrams. Block diagrams provide a means of representing any type of electronic circuit
or system in a simple graphic format. Block diagrams are designed to present flow or functional
information about the circuit or system, not detailed component data. The symbols shown in
Figure 12 are used in block diagrams.
When block diagrams are used, the basic blocks shown above (Figure 12) can be used for
almost anything. Whatever the block represents will be written inside. Note that block
diagrams are presented in this chapter with electronic schematics because block diagrams are
commonly found with complex schematic diagrams to help present or summarize their flow or
functional information. The use of block diagrams is not restricted to electronic circuits. Block
diagrams are used extensively to show complex instrument channels and other complex systems
when only the flowpath of the signal is important.
Examples of Block Diagrams
The block diagram is the most basic and easiest to understand of all the types of engineering
prints. It consists of simple blocks that can represent as much, or as little, as desired. An
example of a block diagram is shown in Figure 13.
This particular block diagram represents an instrumentation channel used to measure the
neutron flux, indicate the measured flux, and generate output signals for use by other systems.