DIESEL ENGINES
DOE-HDBK-1018/1-93
Diesel Engine Fundamentals
center of the "V" between the two banks of cylinders. In larger or multi-camshafted V-
type engines, the camshafts are usually located in the heads.
Blower
The diesel engine's blower is part of the air intake system and serves to compress the
incoming fresh air for delivery to the cylinders for combustion. The location of the
blower is shown on Figure 2. The blower can be part of either a turbocharged or
supercharged air intake system. Additional information on these two types of blowers is
provided later in this module.
Diesel Engine Support Systems
A diesel engine requires five supporting systems in order to operate: cooling, lubrication, fuel
injection, air intake, and exhaust. Depending on the size, power, and application of the diesel,
these systems vary in size and complexity.
Engine Cooling
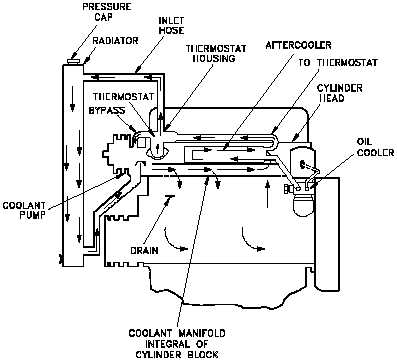
Figure 11 Diesel Engine Cooling System
Nearly all diesel
engines rely on a
liquid
cooling
system to transfer
waste heat out of
the
block
and
internals as shown
in Figure 11. The
cooling
system
consists of a closed
loop similar to that
of a car engine and
c o n t a i n s
t h e
following
major
components: water
pump, radiator or
heat
exchanger,
water jacket (which
consists of coolant
passages
in
the
block and heads),
and a thermostat.
ME-01
Rev. 0
Page 12