Rf
N
f
f
Rf
N
1.29 x 1012
fissions
cm3 sec
1 x 1020atoms
cm3
3 x 1013
neutrons
cm2 sec
4.3 x 1022 cm2
1 barn
1 x 1024 cm2
430 barns
1 watt
1 erg
1 x 107 watt sec
1 MeV
1.602 x 106erg
1 fission
200 MeV
3.12 x 1010fissions
second
REACTION RATES
DOE-HDBK-1019/1-93
Reactor Theory (Neutron Characteristics)
NP-02
Page 20
Rev. 0
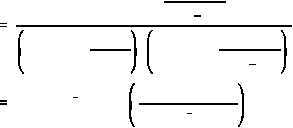
Step 2:
To find the microscopic cross section, replace
with (N x
) and solve
f
f
for
.
f
Reactor Power Calculation
Multiplying the reaction rate per unit volume by the total volume of the core results in the total
number of reactions occurring in the core per unit time. If the amount of energy involved in each
reaction were known, it would be possible to determine the rate of energy release (power) due
to a certain reaction.
In a reactor where the average energy per fission is 200 MeV, it is possible to determine the
number of fissions per second that are necessary to produce one watt of power using the
following conversion factors.
1 fission
=
200 MeV
1 MeV
=
1.602 x 10 ergs
-6
1 erg
=
1 x 10 watt-sec
-7
This is equivalent to stating that 3.12 x 10 fissions release 1 watt-second of energy.
10