TYPES OF FORCE
Application of Newton's Laws
CP-04
Page 20
Rev. 0
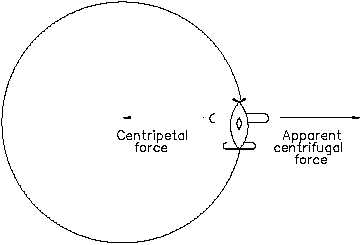
Figure 11 Centrifugal Force
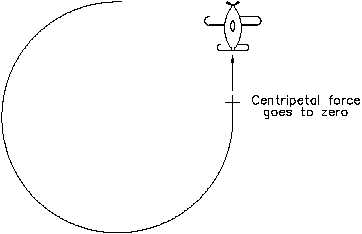
Figure 12 Loss of Centripetal Force
Centrifugal Force
Another force, which appears
to be opposite the direction of
motion, is the centrifugal force
acting on an object that follows
a curved path. This force
appears to be a force directed
away from the center of the
circular path. This is actually a
fictitious force, but is an
apparent force that is used to
describe the forces present due
to an object's rotation.
To
better
understand
centripetal
and centrifugal
forces, consider that a string is
attached to the plane in Figure
10. As the plane rotates about the center, the string places a centripetal force on the plane. This
causes the plane's velocity to change in direction, thus causing it to travel in a circle.
The apparent outward force,
centrifugal force, seems to pull
the plane away from the center
shown in Figure 11. This is the
same apparent outward force
one feels when riding in a car
when the car travels in a circle.
It
can
be
proven
that
centrifugal force is not
an
actual force by cutting the
string. In doing so, the plane
will fly off in a straight line that
is tangent to the circle at the
velocity it had the moment the
string was cut. If there were an
actual centrifugal force present,
the plane would not fly away in
a line tangent to the circle, but
would fly directly away from
the circle (see Figure 12).