GRAPHIC METHOD OF VECTOR ADDITION
Vectors
CP-02
Page 18
Rev. 0
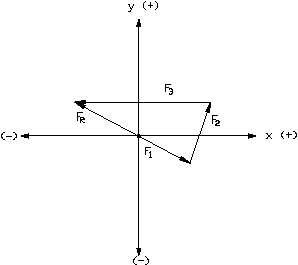
Figure 19 Graphic Addition - Example 1
Step 5.
Determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant.
a.
Measure the displacement and angle directly from the graph using a ruler
and a protractor.
b.
Determine the components of the resultant by projection onto the x- and
y-axes.
Example 1:
What are the magnitude and direction of the resultant for the following: F = 3
1
units at 300 , F = 4 units at 60 , and F = 8 units at 180 ? The three vectors and
o
o
o
2
3
their resultant are shown in Figure 19.
Answer:
F = 4 units at 150
R
o
Example 2:
Given X = 50 Ohms at 90 , R = 50 Ohms at 0 , and X = 50 Ohms at 270 , what
L
c
o
o
o
is the Resultant Z? (See Figure 20) Note: X is inductive reactance, X is
L
c
capacitive reactance and Z is impedance.
Answer:
Z = 50 Ohms at 0o