DC CIRCUIT FAULTS
Basic DC Theory
Short Circuit (Series)
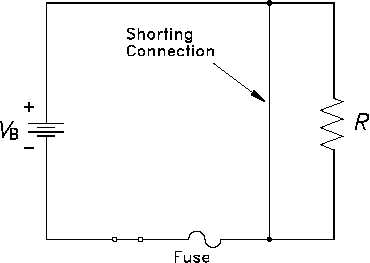
In a DC circuit, the only current limit is the circuit resistance. If there is no resistance in a
circuit, or if the resistance suddenly becomes zero, a very large current will flow. This condition
of very low resistance and high current flow is known as a "short circuit" (Figure 56).
Figure 56 Shorted DC Circuit
A short circuit is said to exist if the circuit resistance is so low that current increases to a point
where damage can occur to circuit components. With an increase in circuit current flow, the
terminal voltage of the energy source will decrease. This occurs due to the internal resistance
of the energy source causing an increased voltage drop within the energy source. The increased
current flow resulting from a short circuit can damage power sources, burn insulation, and start
fires. Fuses are provided in circuits to protect against short circuits.
Short Circuit (Parallel)
When a parallel circuit becomes short circuited, the same effect occurs as in a series circuit: there
is a sudden and very large increase in circuit current (Figure 57).
ES-02
Page 68
Rev. 0